The Complete Guide on Australian Medical School Requirements, ATAR, and More

Table of Contents
Did you know that the average acceptance rate for undergraduate medicine programmes in Australia is just 30%? And that number can drop as low as 10-15% for the most prestigious universities.
These stats show not only how competitive it is to apply for medicine in Australia but also how important it is to understand the Australian medical school requirements in order to maximise your chance of acceptance.
In this blog, we will give you a comprehensive rundown of what applying for medicine in Australia looks like, including the essential deadlines for 2026. We will go over the systems that are used to evaluate students in the country while also providing a comparison with New Zealand. In the end, we will also give you alternative and equally prestigious pathways into medicine that hold up to the rigorous standards for accreditation and international recognition.
What is ATAR?
Before going through the application process for undergraduate medicine in Australia, it is important to understand the Australian Tertiary Admission Rank (ATAR) system.
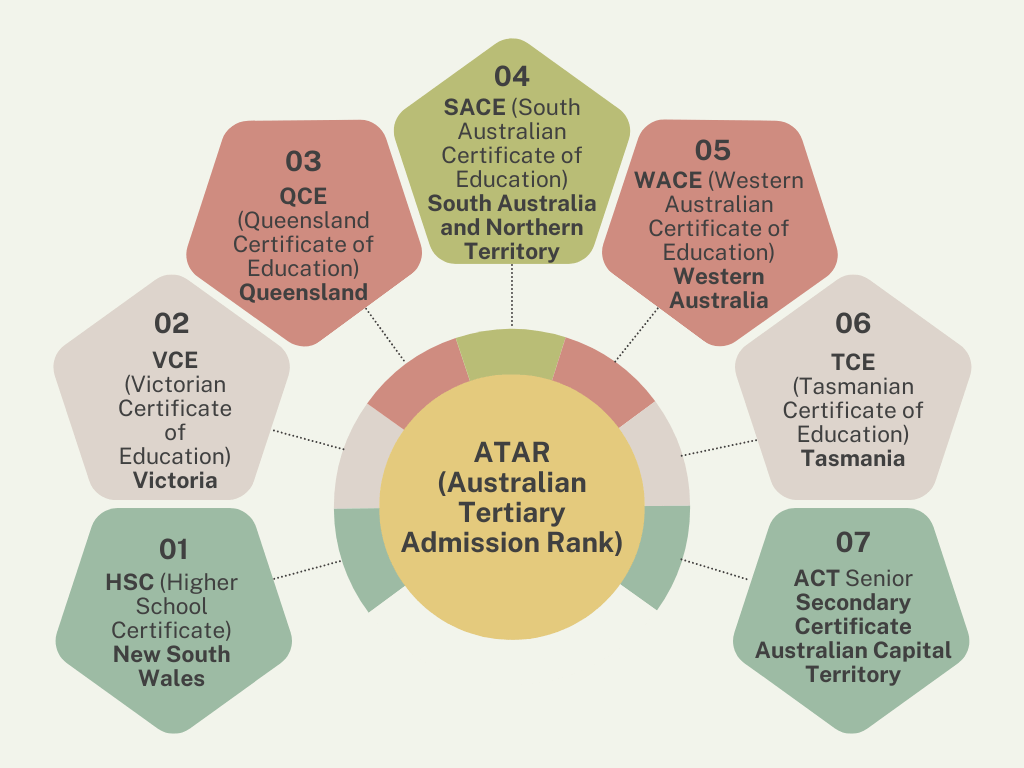
Since Australia is divided into several states, each student receives slightly different certificates when they graduate high school. The ATAR is used to provide a standardised method to measure and rank each student’s overall academic achievement when compared to their peers across the country.
Essentially, once you graduate, you will get a ranking between 0 and 99.95 to show how well you did in high school compared to other students.
Depending on your state, you will receive one of the following certificates upon graduation:
- HSC (Higher School Certificate): Used by students in New South Wales
- VCE (Victorian Certificate of Education): Similar to the HSC, the VCE is the credential awarded to secondary school students who successfully complete high school in Victoria
- QCE (Queensland Certificate of Education)
- South Australia and Northern Territory: In these regions, students complete the SACE (South Australian Certificate of Education)
- Western Australia: Students in Western Australia receive the WACE (Western Australian Certificate of Education)
- Tasmania: In Tasmania, the certificate is known as the TCE (Tasmanian Certificate of Education)
- Australian Capital Territory: Students in the ACT receive the ACT Senior Secondary Certificate

How is ATAR calculated?
The Australian Tertiary Admission Rank involves several steps to ensure a fair and standardised assessment of student's academic achievements, mainly:
- First, your final year examination scores are used as the starting point for your ATAR rank. These scores are based on your performance in specific subjects which will be required by your medical school.
- Since students take different combinations of subjects with varying difficulty across the states, subject scaling will be applied to your scores to achieve a standardised output.
- After subject scaling, the combined score for each student is calculated by summing the scaled scores achieved in their chosen subjects.
- Once the scores for all students are ready, they get ranked in order of performance. Your ranking will be turned into percentiles based on your position in the overall ranking. High-ranking students will get a percentile close to 100 while low-ranking students will get one closer to 0.
- Finally, the percentile rank is converted to an ATAR score between 0 and 99.95 using a conversion table provided by the relevant state or territory's Tertiary Admissions Centre (TAC).
The ATAR is designed to accurately reflect each student's position among his peers, giving universities a fair way to judge applicants.
Adjustment Points
Some universities may also assign adjustment (bonus) points to your ranking depending on several criteria, including:
- Equity considerations to support students from disadvantaged backgrounds or areas.
- High performance in specific year 12 subjects relevant to your degree.
- Living in or attending a school in a designated regional or remote area might qualify you for additional adjustment points.
- Elite athletes and performers may also get points to acknowledge their commitment to balancing their performance with their studies.
The application process for Australian medical schools
Now that you understand how the ATAR works, here are the traditional pathways into medicine in Australia:
For Undergraduate Medicine
If you’re in high school and are looking forward to launching a successful career in medicine, here are the steps that you will typically need to take:
- Finish high school and take your graduation exam
- Receive your ATAR (Australian Tertiary Admission Rank)
- Take the UCAT (University Clinical Aptitude Test)
- Apply for medical school
- Take a medical school interview, which will assess your interpersonal skills, empathy, ethical reasoning, and motivation.
The UCAT is a standardised computer-based admissions test used by universities in Australia and the UK for admissions to medical and dental programmes. It assesses qualities that are considered desirable in health professions, such as cognitive abilities, including critical thinking, problem-solving, and situational judgement. The maximum score for the UCAT is 3600.
It is important to note that not every medical school requires the UCAT. For instance, James Cook University assesses students only based on their previous academic performance and interviews.
For Graduate Entry Medicine
If you already hold a relevant bachelor’s degree in a science-related field, you can apply for graduate entry in Medicine instead. However, you will be assessed based on your GPA (Grade Point Average) rather than your ATAR.
Additionally, you will need to sit the GAMSAT (Graduate Medical School Admissions Test), which is a standardised exam that assesses whether a student is ready to undertake high-level studies in medical programmes. For some programmes, international applicants also have the option to submit their Medical College Admission Test (MCAT) scores instead of taking the GAMSAT.
Finally, before being accepted into a graduate entry medicine programme in Australia, you will also be invited to an interview, similar to those used for undergraduate medicine programmes.
Key requirements for undergraduate medicine in Australia
Although each university has slightly different acceptance criteria, here are the general medical school requirements in Australia:
Core subjects
Typically, the prerequisites for core subjects include a combination of subjects such as Chemistry, Biology, Physics, and Mathematics. However, it is essential to research each medical school you are interested in, as every university has its own unique acceptance criteria. But generally, these are the 4 main subjects you should be focusing on during your final years of high school.
ATAR Scores
Generally, to get accepted into a top medical school in Australia, you will need an ATAR ranking of at least 95.0. The most prestigious universities, like the Sydney Medical School, have an ATAR requirement of 99.5, meaning they will accept only the top 0.5% of students each year.
However, there are also options like La Trobe University’s medical programme, which only has a requirement of an 80.0 unadjusted ATAR score.
UCAT Scores
Typically, you will need a 3000+ UCAT score to be invited to an interview for an undergraduate medical programme in Australia. This means that only the top 90-95% of students get accepted each year.
To be among the top 1% of students, you will need to score at least 3250 points.
How to boost your application
To further enhance your chances of admission, it is also beneficial to engage in extracurricular activities that demonstrate your passion for medicine. Volunteering at hospitals or clinics, participating in medical research projects, or shadowing healthcare professionals can provide valuable experiences and make your application stand out.
Important dates and deadlines for medical school applications
Here are the essential dates you need to know for 2026:
ATAR scores
You can expect to get your scores mid-December, usually between the 14th and 18th of December.
UCAT exam deadlines:
| Mid-May (14th of May in 2026) | UCAT Account creation opens |
| Mid-June (18th of June in 2026) | Booking opens |
| Mid-July (8th of July in 2026) | Testing starts |
| Mid-September (15th of September in 2026) | Access Arrangement application deadline |
| Mid-September (19th of September in 2026) | Booking deadline UCAT Account creation closes |
| Late-September (26th of September in 2026) | Last test day |
| Late-September (27th of September in 2026) | Bursary Scheme application deadline |
| Mid-October (15th of October in 2026) | UCAS deadline |
| Early November | Results delivered to universities |
GAMSAT exam deadlines for March:
| March Test | |
|---|---|
| Registration opens | December |
| Registration closes | 1st of February |
| Exam dates | Written Communication: 9-10 March Humanities & Bio Sciences: 22-24 March |
GAMSAT exam deadlines for September:
| September Test | |
|---|---|
| Registration opens | May |
| Registration closes | 4th of July |
| Exam dates | Written Communication: 31st of August - 1st of SeptemberHumanities & Bio Sciences: 13-15 of September |
Medical school application deadlines
Typically, between late September and late January, depending on the university.
Differences between Australian and New Zealand medical school requirements
Although both the UCAT and GAMSAT are used in both countries, the ATAR is not accepted in New Zealand. Instead, high school students there receive an NCEA (National Certificate of Educational Achievement), which they can use to apply for medical school in either country.
The NCEA has 3 levels:
NCEA Level 1: Typically undertaken in Year 11 (the 11th year of schooling).
NCEA Level 2: Usually in Year 12.
NCEA Level 3: Generally in Year 13 (the final year of secondary school).
After graduating, students in New Zealand use their NCEA to gain University Entrance (UE), which is the minimum requirement for admission to most degree-level programmes at universities.
UE has a specific set of requirements and is not automatically granted. Instead, it requires meeting specific standards:
- Achieve NCEA Level 3.
- Gain 14 credits in each of three subjects from the list of approved subjects. These are usually taken at Level 3.
- Achieve literacy requirements: 10 credits at Level 2 or above in English or Te Reo Māori, with at least 5 credits in reading and 5 credits in writing.
- Achieve numeracy requirements: 10 credits at Level 1 or above.
Once students have gained University Entrance, they can apply for admission to New Zealand universities. Universities will consider their NCEA results (including Level 3 and UE) as part of the admission process.
In order to be eligible to apply for medical school in Australia as a New Zealand candidate, you will need NCEA Level 3.
Top-Tier Options for Medicine Beyond Australia
It is safe to say that getting accepted to study Medicine or Dentistry in Australia is extremely competitive, and only a small number of students get in each year. However, you shouldn’t let that stop you from chasing your dreams of becoming a doctor or dentist because there are many world-class alternatives available for you to start studying in 2026.
For instance, Europe is widely recognised as the top destination for medical education in English and offers affordable, accredited and internationally recognised programmes in both medicine and dentistry.
Another viable pathway into medicine is studying in the Caribbean, which has emerged as a high-quality option thanks to the significant recent efforts and investments done by local governments and international programmes. The universities in the region offer top-tier graduate entry options for medicine, which are often compared to and follow the rigorous standards of the US medical education system. Additionally, the medical schools in the Caribbean also offer undergraduate options via pre-medicine courses that will thoroughly prepare you for your studies.
At Medlink Students, we offer free consultations with one of our expert academic advisors, who can help you find the perfect university for you. We work closely with 100+ of the best medical schools in Europe and the Caribbean, and we can save you countless hours of research with a simple, pressure-free chat.
We have over a decade of experience and have successfully guided over 15,000 towards becoming successful doctors or dentists. Sign up for a free consultation today and find out how we can help you achieve your dreams.
Conclusion
Although it is difficult, it is by no means impossible to secure your spot at one of the many prestigious medical universities in Australia. However, you will need to be dedicated and put in the effort to turn your ambitions into reality. Hopefully, after reading this blog, you now understand the Australian medical school requirements, as well as how the ATAR system works, and what scores you have to shoot for to get accepted.
Remember, even if things don’t work out in Australia, there are always incredible options available for you beyond the land down under.
Q&A: Australian Medical School Requirements
1. What is the average acceptance rate for undergraduate medicine programs in Australia?
The average acceptance rate for undergraduate medicine programs in Australia is approximately 30.1%, with prestigious universities often having even lower acceptance rates, ranging from 10-15%.
2. What is the ATAR, and how is it used in the Australian education system?
The ATAR (Australian Tertiary Admission Rank) is a standardised ranking used to measure and rank students' overall academic achievement compared to their peers across the country. It provides a ranking between 0 and 99.95 based on students' performance in their final year of high school.
3. How is the ATAR calculated?
The ATAR calculation involves several steps, including using final year examination scores as a starting point, applying subject scaling to achieve standardised scores, ranking students based on their performance, and converting their percentile rank into an ATAR score.
4. What are the traditional pathways into undergraduate medicine in Australia?
For undergraduate medicine, the traditional pathway involves completing high school, obtaining an ATAR, taking the UCAT (University Clinical Aptitude Test), applying for medical school, and attending a medical school interview to assess interpersonal skills and motivation.
5. What are the key requirements for undergraduate medicine in Australia?
Core subjects typically include Chemistry, Biology, Physics, and Mathematics, with specific ATAR and UCAT score requirements varying among universities.
6. How do medical school requirements in Australia differ from those in New Zealand?
While both countries use admission tests like the UCAT and GAMSAT, New Zealand does not use the ATAR. Instead, students receive an NCEA (National Certificate of Educational Achievement) and gain University Entrance (UE) to apply for medical school.
7. What are some top-tier options for studying medicine beyond Australia?
Europe and the Caribbean offer world-class medical education programs in English, providing affordable, accredited, and internationally recognised pathways into medicine. Medlink Students offers free consultations to assist students in finding the perfect university for their medical studies.
8. Can international students apply to Australian medical schools, and are there additional requirements for them?
Yes, international students can apply to Australian medical schools, but they may have additional requirements such as English language proficiency tests (e.g., IELTS, TOEFL) and visa regulations. Additionally, they can provide their MCAT scores instead of sitting the UCAT.
9. Are there specific extracurricular activities or experiences that can strengthen a medical school application in Australia?
You can strengthen your medical school application by engaging in extracurricular activities such as volunteering at hospitals or clinics, participating in medical research projects, or shadowing healthcare professionals can enhance a medical school application by demonstrating commitment and passion for medicine.
10. Does Australia have graduate entry options into Medicine? What are the requirements?
Absolutely, there are many high-quality options available for graduate entry into medicine in Australia. However, you will be assessed based on your GPA rather than your ATAR ranking. Additionally, you will need to sit the GAMSAT exam and participate in an interview.
Leave a Reply

About Medlink Students
Leading international recruitment company for medical students in Europe. British Council Certified Agents. 10+ years of experience and more than 10,000 students advised.








