MBBS vs MD: Differences, Entry Requirements & Career Paths

A great question we get a lot from students is: “MD vs MBBS, which is better for me?”
After all, you’re setting the foundation for your entire medical career, so it’s important to know what you’re getting into. However, the answer can be a bit confusing, as the MD degree has a different meaning in the US/Canada and Europe.
That’s why in this blog, we’ll go through all the differences between MBBS and MD, including which one you should go for depending on where you want to become a doctor, their entry requirements, curricula differences, and more. By the end, you’ll be able to choose with confidence and take the next step towards your dream career in medicine.
The key takeaways of this blog include:
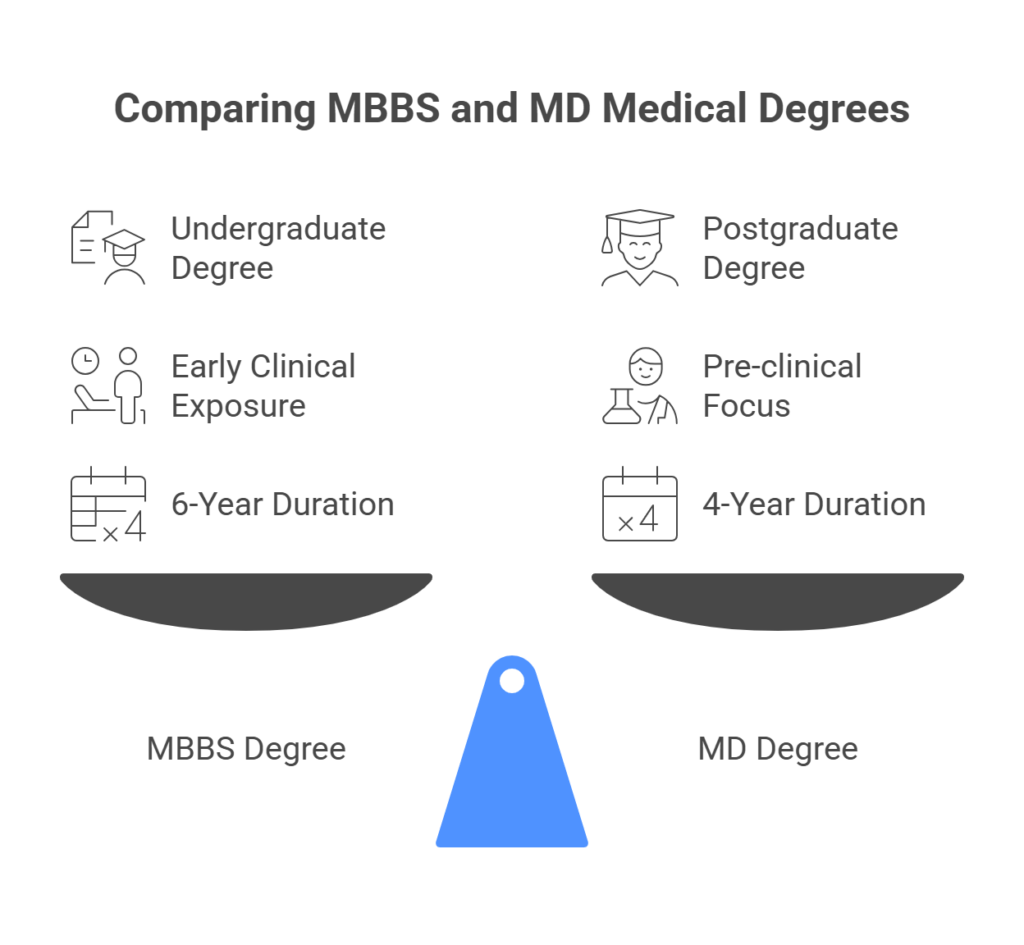
- MBBS and MBChB are 6-year undergraduate medical programmes taken directly after high school.
- MD in Europe is typically the same as MBBS.
- MD in North America is a 4-year postgraduate medical programme for which you need to already have a Bachelor’s Degree.
- Both are internationally recognised medical degrees that will enable you to become a doctor with the right steps. This usually includes passing licensing exams, and registering with the local medical council.
Table of Contents
- 1 What Are MBBS and MD?
- 2 MBBS Degree vs MD Entry Requirements
- 3 MD vs MBBS vs MBChB Career Pathways & Recognition
- 4 MBBS vs MD in a Nutshell
- 5 Why This Matters to You
- 6 FAQ - The MBBS vs MD Debate
- 6.1 What is the difference between an MBBS vs MD doctor degree?
- 6.2 Which is better: MD vs MBBS vs MBChB?
- 6.3 How long does it take to complete MBBS vs MD degrees?
- 6.4 Can an MBBS graduate work in the US?
- 6.5 What’s the MD degree vs MBBS global recognition?
- 6.6 How do I choose between MBBS vs MD vs DM?
- 6.7 What are the entry requirements for MD degree vs MBBS in different regions?
- 6.8 Can I specialise immediately as an MD doctor vs MBBS graduate?
- 6.9 What are the key factors in the MBBS vs MD vs MBChB decision?
What Are MBBS and MD?
Let’s get straight into the differences between the MBBS vs MD degree and their specifics. For all UK students wondering about MBChB, don’t worry, we’ve got you covered too.
MBBS Degree
The complete form of MBBS is Bachelor of Medicine or Bachelor of Surgery.
It’s an undergraduate medical degree typically entered straight after high school or after a pre-med course. MBBS typically lasts 6 years and is awarded throughout Europe, Australia, India and more.
The curriculum of this degree combines foundational sciences with early clinical exposure for a comprehensive educational experience that incorporates internships/clerkships and leads directly into foundational training, more internships, and/or specialisation.
MBBS is an internationally recognised degree that is accepted worldwide, as long as you’ve graduated from a reputable medical school with accreditation and recognition.
Fill in this form if you want a free consultation about your options to study medicine in Europe or the Caribbean:
Check your email to Book a FREE call
with an expert advisor
Look at your promotions/spam folders, just in case.
MD Degree
MD in the US. Canada and the Caribbean
Doctor of Medicine is the primary medical qualification in North America, but unlike in Europe, MD is a 4-year postgraduate degree. This means that you need to already have an undergraduate degree in a relevant discipline, preferably in 1 of the health-related sciences.
The MD curriculum is structured around 2 pre-clinical years, focusing on foundational medical sciences, followed by 2 clinical years of hands-on patient care. Upon graduation, MD holders apply through the residency matching process to proceed into a residency training programme.
Just like MBBS, the postgraduate MD degree is recognised throughout the world, as long as you’ve graduated from a reputable medical school.
MD in Europe
In many European countries, like Poland, Bulgaria, Romania, etc., the primary medical qualification is also called MD. It is a 6-year Master’s degree equivalent to MBBS/MBChB, taken straight after secondary school.
The true postgraduate research doctorate (taken after MBBS/MD) is generally called DM (Doctorate of Medicine), or a PhD in Medicine, depending on the country.
MBChB Degree
If you’re from the UK, you’ve probably read a thread or 2 discussing MBChB vs MBBS vs MD. However MBChB (Medicinae Baccalaureus, Baccalaureus Chirurgiae) is simply another name for the same undergraduate medical degree as MBBS.
It lasts 5-6 years and is awarded in many UK, Irish and Commonwealth universities. The curriculum, clinical exposure and global recognition mirror the MBBS pathway. After graduation, MBChB holders typically go into their Foundation Year Training (FY1 & FY2).

MBBS Degree vs MD Entry Requirements
The starting point (a.k.a. the requirements) is the biggest difference between MD vs MBBS.
MBBS Entry Requirements
If you’re coming straight from high school, then going for an MBBS/MBChB/European MD degree is the most straightforward. Typically, you will need:
- A high-school diploma with good grades in Biology, Chemistry, and sometimes Physics, Mathematics (A-levels for UK students).
- To take an entrance exam and/or interview (not always).
- A strong application, preferably with extracurricular experience in a healthcare setting.
- English language proficiency. Proven either via certification or with a test.
MD Entry Requirements (US/Canada)
By contrast, the requirements for the MD track in the US or Canada are:
- Having an undergraduate degree. Typically, any discipline is fine as long as you have the prerequisite science courses in Biology, Chemistry, and Physics.
- Passing the MCAT (Medical College Admission Test), a standardised test. However, not all universities require taking the MCAT.
- Having a holistic student profile for medicine. Strong GPA, relevant extracurriculars (clinical experience, research) and a compelling personal statement.
- Passing an interview. Usually via Multiple mini-interviews (MMIs) or traditional panels to assess communication, ethical reasoning, and compatibility with the medical profession.
MD vs MBBS vs MBChB Career Pathways & Recognition


Choosing between MD degree vs MBBS will not only determine your medical training but can also greatly help you on your career trajectory.
Naturally, if you want to become a doctor in Europe, it would be an advantage to study there, but that doesn’t mean that a US MD degree wouldn’t get the job done. In that same way, studying in North America or the Caribbean can give you an advantage when getting your licensure. However, that doesn’t mean that if you get an MBBS degree in Europe, you won’t be able to get licensed in the US.
In fact there are many European medical schools that cater to Americans/Canadians and students that wish to become doctors in the US.
Here's how the paths typically unfold for MBBS and MD graduates.
MBBS/MBChB Graduates
After completing the MBBS/MBChB degree, graduates move into clinical training based on the country they’ve studied in.
For example, In the UK, graduates must register with the General Medical Council (GMC) to obtain their Foundation Year 1 (FY1) licence. In India, MBBS holders register with the Medical Council of India (MCI) or the National Medical Commission (NMC) before beginning their internship year.
Once the degree is complete, MBBS graduates enter structured foundation or internship programmes, with no separate residency match process required. In the UK, the Foundation Years provide hands-on experience in various medical fields. In Europe, graduates often opt to pursue a postgraduate qualification, which allows them to specialise in areas like surgery, internal medicine, or paediatrics.
MBBS graduates who wish to secure a clerkship or practise internationally typically just need to pass additional exams, such as the USMLE for the United States or the PLAB/UKMLA exams to practise in the UK. This added layer of qualification is necessary to ensure all international graduates meet the standards and regulations of their new host country.
MD Graduates
MD graduates in North America and the Caribbean follow a more structured postgraduate path.
After completing their degree, they enter residency training, where they specialise in fields such as internal medicine, surgery, or paediatrics. This process is facilitated through the National Residency Match Program (NRMP). Another option that some MD graduates choose is to combine clinical training with research, pursuing an MD/PhD track that prepares them for both medical practice and scientific study
Just like International Medical Graduates, once their residency is complete, MD holders must pass the USMLE exams and obtain a state medical license before they can practise independently. This ensures that they meet the professional standards required to treat patients safely and effectively.
After completing residency, MD graduates have opportunities to pursue advanced specialisation through fellowships. These fellowships allow doctors to deepen their expertise in their preferred area. This advanced training is essential for those who wish to practise at the highest levels in highly specialised medical fields.
If you’re curious about the differences in specialisation pathways in Europe, the US and the UK, we’ve got a comprehensive guide on How to Become a Dermatologist: Pathways, Cost & Timeline
MBBS vs MD in a Nutshell
Here’s a recap of the MBBS vs MD main differences:
| Feature | MBBS | MD (in North America) |
| Full form | Bachelor of Medicine, Bachelor of Surgery | Doctor of Medicine |
| Level | Undergraduate entry after high school | Postgraduate entry after a bachelor’s degree |
| Typical duration | 6 years | 4 years |
| Curriculum focus | Early patient contact; integrated basic sciences & clinical training | 2 pre-clinical years and 2 clinical clerkships; intensive residency |
| Entry requirements | A-levels/High-school grades + English proficiency + entrance exam/interview (not always) | Bachelor’s degree + MCAT + holistic review + interviews |
| Postgraduate training | Direct into foundation/internship programmes or speciality training | Matched into residency via NRMP; option for MD/PhD |
| Registration & recognition | Register with the local medical council and pass any necessary exams for licensure | Must pass USMLE Steps 1–3 and obtain a state licence |
| Global mobility | Internationally recognised | Internationally recognised |
Why This Matters to You
Imagine investing years and tens of thousands in tuition, only to discover mid-course that your chosen degree won’t qualify you for your dream speciality. You could find yourself bogged down repeating modules, scrambling for costly licensing exams, or facing closed doors to the specialities you’ve always wanted.
At Medlink Students, we make sure that doesn’t happen. Our expert advisors will assess your academic background, career goals and preferred destinations to recommend the precise MBBS or MD pathway that aligns with your ambitions. Our Student Success Programme offers complete medical school guidance to help transform your uncertainty into confidence through a clear and concise plan.
Sign up for a free consultation with 1 of our academic advisors and we’ll help you step into medical school knowing you’ve made the right choice.
FAQ - The MBBS vs MD Debate
What is the difference between an MBBS vs MD doctor degree?
MBBS (Bachelor of Medicine, Bachelor of Surgery) is an undergraduate medical degree offered in European countries, Australia, India, etc. Meanwhile, MD (Doctor of Medicine) in the US and Canada is a postgraduate degree taken after a bachelor’s degree. In much of Europe, however, MD is also an undergraduate-entry degree equivalent to MBBS/MBChB.
Which is better: MD vs MBBS vs MBChB?
There’s no one-size-fits-all “better.” MBBS and MBChB are almost identical in curriculum and recognition in many parts of the world. A US-style MD gives you a focused 4-year medical school plus residency, while a European MD mirrors MBBS with early clinical exposure. Your choice depends on your target country, preferred timeline and long-term goals.
If you would like to know what’s best for your goals and ambitions, we offer free consultations with our expert academic advisors. Sign up for a call here.
How long does it take to complete MBBS vs MD degrees?
An MBBS/MBChB (and European MD) lasts for 6 years, including clinical rotations and usually an internship. A US/Canada MD takes 4 years of medical school followed by 3–7 years of residency.
Can an MBBS graduate work in the US?
Yes, you can work in the US with an MBBS degree, but you’ll need to pass the USMLE Steps 1, 2 and secure state licensure. If you’re planning on studying in Europe, many European medical schools offer dedicated USMLE prep courses to help students transition smoothly into North American practice.
What’s the MD degree vs MBBS global recognition?
Both are internationally recognised degrees. The important part is graduating from a reputable medical school with accreditation, recognition and a strong curriculum.
How do I choose between MBBS vs MD vs DM?
MBBS/MD (undergraduate or US-style) gives you your primary knowledge and degree. DM (Doctorate of Medicine) is akin to a PhD taken after MBBS/MD, not a substitute for them. Pick between MBBS Degree vs MD first, then consider DM if you want a PhD speciality pathway later.
What are the entry requirements for MD degree vs MBBS in different regions?
For MBBS, MBChB, and European MD you need a high school diploma with good grades or solid A-levels in Biology, Chemistry, and sometimes Mathematics, Physics.
For the postgraduate MD in North America you need a Bachelor’s Degree, MCAT, strong GPA, extracurriculars and interviews.
Can I specialise immediately as an MD doctor vs MBBS graduate?
North American MD graduates match directly into residency and can specialise via fellowships. MBBS/European MD holders enter foundation or internship programmes, then apply for speciality training posts.
What are the key factors in the MBBS vs MD vs MBChB decision?
Consider your desired practice location, how quickly you want to start patient care, programme length, cost and research opportunities. Mainly for choosing between MD vs MBBS doctor degree decide whether you prioritise early clinical immersion you get with European programmes or a structured 50/50 approach in North America.
Leave a Reply


About Medlink Students
Leading international recruitment company for medical students in Europe. British Council Certified Agents. 10+ years of experience and more than 10,000 students advised.








